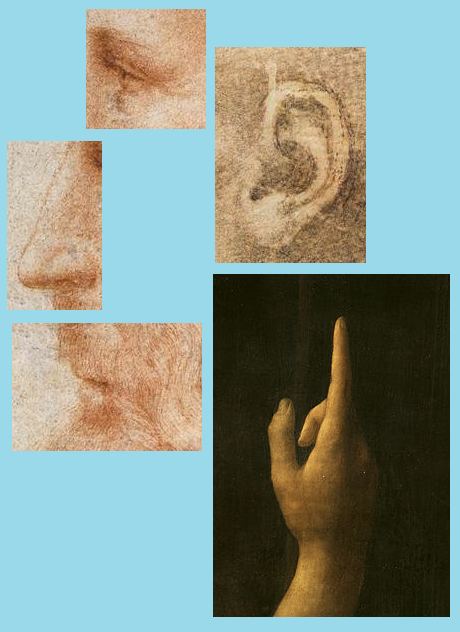
If you aim to be an author, you must observe the world as a writer does. You’ll write better stories if you do.
When I use the word ‘observe’ I mean it in the general sense of perceiving by one or more of the five senses (or beyond those five, even). I’ve blogged before about conveying the five senses in your stories, but here I’m referring not to your characters, but to you perceiving the real world.
 Before we get to writers, let’s discuss observation in general. While acknowledging there are other epistemological theories, I’ll assume there is a single, physical world out there, and each person observes it differently. Those differences are due to observations taken from different physical locations, accuracy of senses, mood, previous experiences, and many other things.
Before we get to writers, let’s discuss observation in general. While acknowledging there are other epistemological theories, I’ll assume there is a single, physical world out there, and each person observes it differently. Those differences are due to observations taken from different physical locations, accuracy of senses, mood, previous experiences, and many other things.
Observation, then, is a combination of a signal from one or more senses, and the mental activity resulting from the signal. We perceive with our senses and our brains.
Early in life, we discover the universe is too big and filled with too much stuff for us to see every little detail, so we learn to filter some things out. We focus on the parts we find most useful.
We recognize patterns, and form mental models of how the world is. That way we can tell at a glance if something doesn’t fit, and we can fill in the details we can’t sense but assume are there. Some people hone their senses to a fine degree of accuracy through practice, and some do not.
What does it mean to observe the world as a writer does? A good writer:
- Considers the world as a source of story ideas, details, and descriptions;
- Sees places as potential story scenes;
- Notices people and incorporates aspects of them in story characters;
- Hears all talking as potential dialogue;
- Watches people when they’re experiencing intense emotions, so as to pick out appropriate appearance, expressions, and gestures for story characters;
- Tastes food with the intent to describe it as a meal in a story;
- Picks out the most telling details in real places or people, so as to better describe scenes and characters;
- Goes ‘people-watching’ and imagines background stories for the observed people; and
- Practices observing with all senses to improve both sensing accuracy and the ability to describe in words what is sensed.
You might doubt this advice will help in your particular case. Maybe the scenes in your stories look nothing like the world you live in, and your novel’s characters are completely unlike anyone you know or see. That’s common when writing fantasy or science fiction.
Even in such cases, it benefits you to practice and improve your powers of observation. That ability to pick out and convey the right details, in a manner that transports the reader to your fictional world, will help you no matter how unusual your scenes and characters are.
For further study, I recommend you read this WikiHow article and also this post by Maria Popova.
If you practice perceiving the world and people around you, really strive to develop that skill, one day you might achieve the acute observational prowess of—
Poseidon’s Scribe