The Hero’s Journey is one of the most basic plot types in literature. In 2013, author John Green discussed the hero’s journey in his commencement address at Butler University. In my view, he presented an incomplete view.

In 1949, Joseph Campbell introduced his analysis of the hero’s journey in his book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces. Campbell’s analysis was a complex one, with no less than seventeen stages of the journey.
At the Butler commencement, Mr. Green said that most people consider the hero’s journey to be from a state of weakness to a state of strength. He contended the opposite was true, that heroes begin with strength and end with weakness.
“The real hero’s journey is the journey from strength to weakness…Many of you, most of you, are about to make that journey. You will go from being the best-informed, most engaged students at one of the finest universities around to being the person who brings coffee to people, or a Steak n Shake waiter…That is the true hero’s errand–strength to weakness. And because you went to college, you will be more alive to the experience, better able to contextualize it and maybe even find the joy and wonder hidden amid the dehumanizing drudgery.”
I get what Mr. Green was trying to do in the context of a college commencement. He was preparing the graduates for an upcoming period of weakness. Further, he was telling them they would be better people for having thus suffered. Granted, that’s a valuable teaching point.
Let’s take a moment to define what we mean by “strength” and “weakness.” The most obvious connotation is physical. But we can also speak of strength and weakness in the following areas: mental, spiritual, emotional, overall character, and others.
In most hero’s journey tales, the hero will pass from strength to weakness in at least one of those planes. He or she will reach a place of utter weakness and vulnerability of some kind (or multiple kinds) at some point in the story. Either the antagonist or the environment will bring the hero down.
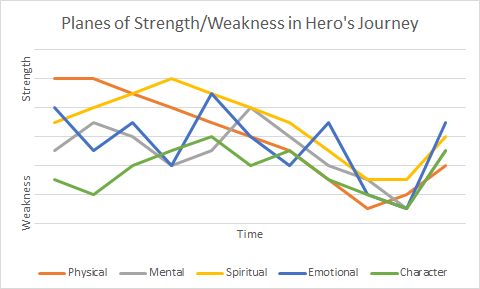
But the story never ends there, does it? It’s not a very heroic tale if the bad guy wins. The hero must pick himself up from the bloody boxing ring mat, or she must summon all her courage from somewhere in misery’s abyss, to rise above the situation. The hero must achieve, through personal toil, a kind of strength at the end.
That final strength can include nuance, of course. The defeat of the antagonist can come with a new understanding of the world’s complexities—the bad guy might have had some valid point among his faults, a point deserving exploration. Or perhaps the hero, having sailed his ship through the perfect storm, might come to a realization that he would never do such a thing again.
Such nuance doesn’t constitute a return to weakness, however. On balance, the hero must end in a position of strength.
With respect to the author of The Fault in Our Stars, Mr. Green should not have stopped at weakness in his address. What a gloomy view of life he gave those graduates! He should have bent the curve upward at the end, should have said heroes move from initial strength to weakness, and on to final strength. He should have told them what happens after the “dehumanizing drudgery.”
Sorry, Mr. Green, but hero’s journey tales have to end with strength. That’s the opinion of—
Poseidon’s Scribe
Note: You’ve gone and done it now. You’ve waited until the very last day of the Smashwords ½ price sale. Tomorrow my books return to full price. Today is your day to be a hero. Pick yourself up from the depths of procrastination and, with your last ounce of strength, surf here, click on a book or two, and use the code they give you at checkout to get the discount.
procrastination and, with your last ounce of strength, surf here, click on a book or two, and use the code they give you at checkout to get the discount.

 Your mind is filled with raw feelings, and you have no room for anything else. You can’t be creative, not now. You can’t get in the mind of a character right now, can’t be bothered with rules of English, or with choosing the right words. Besides, your novel is a comedy, and you’re feeling the opposite of funny.
Your mind is filled with raw feelings, and you have no room for anything else. You can’t be creative, not now. You can’t get in the mind of a character right now, can’t be bothered with rules of English, or with choosing the right words. Besides, your novel is a comedy, and you’re feeling the opposite of funny. In Twain’s acerbic style, he starts by accusing three Cooper-praising reviewers of never having read the books. He then lays into Cooper, saying, “…in the restricted space of two-thirds of a page, Cooper has scored 114 offenses against literary art out of a possible 115. It breaks the record.” Twain asserts there are 19 or 22 rules “governing literary art in domain of romantic fiction” and says Cooper violated 18 of them. He lists those 18 rules.
In Twain’s acerbic style, he starts by accusing three Cooper-praising reviewers of never having read the books. He then lays into Cooper, saying, “…in the restricted space of two-thirds of a page, Cooper has scored 114 offenses against literary art out of a possible 115. It breaks the record.” Twain asserts there are 19 or 22 rules “governing literary art in domain of romantic fiction” and says Cooper violated 18 of them. He lists those 18 rules.