As the old saying goes, if you want to make a small fortune by writing fiction, start with a large fortune. Spoiler alert—the answer to this post’s title question is ‘yes.’
The Problem
Fiction writers should get paid more than most of them do. Consider the loneliness of writing, the struggle to gather the right words—out of many thousands—and to arrange them in just the right order, the trepidation of submitting a manuscript, the anxious anticipation of awaiting a response, the crushing despair of rejection.
Mere doctors and lawyers, accustomed to their lives of ease, could never stand the strain. Yet, by the most paradoxical injustice of our universe, members of these professions earn much more money than most fiction writers.
The Plea
As mentioned in an article in The Guardian, author Philip Pullman wrote an open letter to British publishers, imploring them to pay writers more. He made his case on the basis of fairness, stating that it’s in everyone’s interest to ensure authors can make a living.
Plan A
The uncaring and indifferent among you might ask where the money (these additional funds for deserving authors) should come from. The letter doesn’t cover that matter in detail because the answer is obvious. After all, publishers spend most of their time luxuriating in their vaults, counting and recounting their excess money. They use bills as scrap paper. They use gold coins to shim the legs of wobbly desks. They’re awash in cash, drowning in it.
The letter doesn’t ask publishers to part with all their money, just enough so starving writers can eat. It’s not too much to ask. Publishers will still retain plenty of scrap paper and desk-propping coins.
Plan B
On the off chance those skinflint publishers decline to cough up the necessary funding, the letter hints at another source. Pullman states it’s in ‘everyone’s interest’ to get writers paid appropriately.
Therefore, if publishers prove too stingy, we can turn to Plan B—take money from everyone and spread that sum among writers. However, Plan B may prove more difficult than it sounds. Going door to door with a tin cup strikes me as time-consuming. Also, a few citizens may hold differing opinions of fairness and disagree about what constitutes ‘everyone’s interest.’ Some might even refuse to contribute to the tin cup.
Let’s forget that method and select a far more efficient way of collecting money from ‘everyone’—taxation. We can simply persuade politicians (well known for their powers of logical reason and their sense of fairness) to raise sufficient taxes to pay writers what we’re worth. If they balk at a tax hike, they can feel free to add to the rather minuscule national debt, for payment later, by someone else.
What a grand project! Who’s with me?
The Consequences
Before we march on Washington, there’s one more thing. Failure in this endeavor is not an option. Mr. Pullman’s letter warns that if writers don’t get paid more, they will become an endangered species.
Writers, you may be aware, have almost split off from Homo sapiens to constitute a separate species—Homo scriptor. Failure to pay writers a living wage, Mr. Pullman believes, will cause that species’ population to decline.
What higher purpose does government serve, I ask you, than to protect all the species of the Earth? The endangerment of a beloved species, the possibility of its extinction, should prompt all non-writers to beg their governments to do something to ‘Save the Writers.‘ (Not a bad slogan. I should write that down.)
Rethinking the Problem
As I ponder this, a countervailing thought occurs. As the population of Homo scriptor dwindles, they will produce fewer new books. In a free market, when supply shrinks and demand stays steady or increases, the price goes up. As the price rises, more money should flow to the remaining writers, thus solving their income problem.
In fact, it’s possible this has already happened, and that the world has already reached an equilibrium, with the right number of writers all earning their fair share in a competitive market.
Well, isn’t that a buzz kill? I had my bags packed to march on D.C. Maybe, contrary to Mr. Pullman’s contention, things are as fair as they’re going to be for writers.
And if they’re not, the words of my father keep coming back. He used to ask me, “Who told you the world was fair?” That was a long time ago, before I became—
Poseidon’s Scribe


 Allow me to define what I mean by censorship. It’s the deliberate alteration of text, without the author’s permission, to make the story less offensive to the censor. This is not what a normal editor does. Editors collaborate with authors to correct errors, to make the book as good as it can be.
Allow me to define what I mean by censorship. It’s the deliberate alteration of text, without the author’s permission, to make the story less offensive to the censor. This is not what a normal editor does. Editors collaborate with authors to correct errors, to make the book as good as it can be.
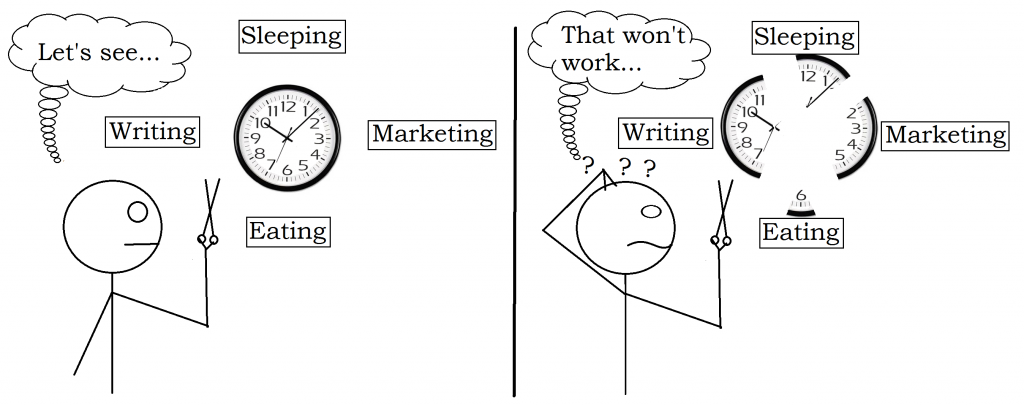 Well, you’d better make time for it. Somehow. Sure, you want to spend your precious time writing and you don’t like marketing. That’s why you became a writer. Still, it turns out that your preferences don’t really enter into this—you must do most of your own marketing (or pay someone to do it for you).
Well, you’d better make time for it. Somehow. Sure, you want to spend your precious time writing and you don’t like marketing. That’s why you became a writer. Still, it turns out that your preferences don’t really enter into this—you must do most of your own marketing (or pay someone to do it for you).



