Today I’m exploring the world of disaster fiction. There are many, many stories dealing with disasters, from local misadventures to world-wide calamities. I’ll discuss frequently occurring themes in disaster fiction, as well as the reasons people read it. That might help you decide if you want to write such a tale.
 First, no disaster story is truly about the disaster. If you want to write about disasters, try non-fiction. As I’ve said before, fiction is about the human condition, so your disaster story is really about the characters, their attempts to cope with the disaster, and how they grow or change as a result.
First, no disaster story is truly about the disaster. If you want to write about disasters, try non-fiction. As I’ve said before, fiction is about the human condition, so your disaster story is really about the characters, their attempts to cope with the disaster, and how they grow or change as a result.
I’ll make a distinction between disaster stories and post-apocalyptic stories. In the latter, the disaster has already occurred and people are trying to handle the aftermath. In the former, the disaster occurs during the story. I’ll discuss post-apocalyptic fiction in a future blog post.
Types
Though disaster stories are about people, we can still classify them by the type of disaster that occurs, and there are plenty to choose from. You might think all the best disasters have been taken already and the reading public won’t go for one more disaster novel. You’d be wrong; since the stories are about people, there are always infinitely more stories to write.
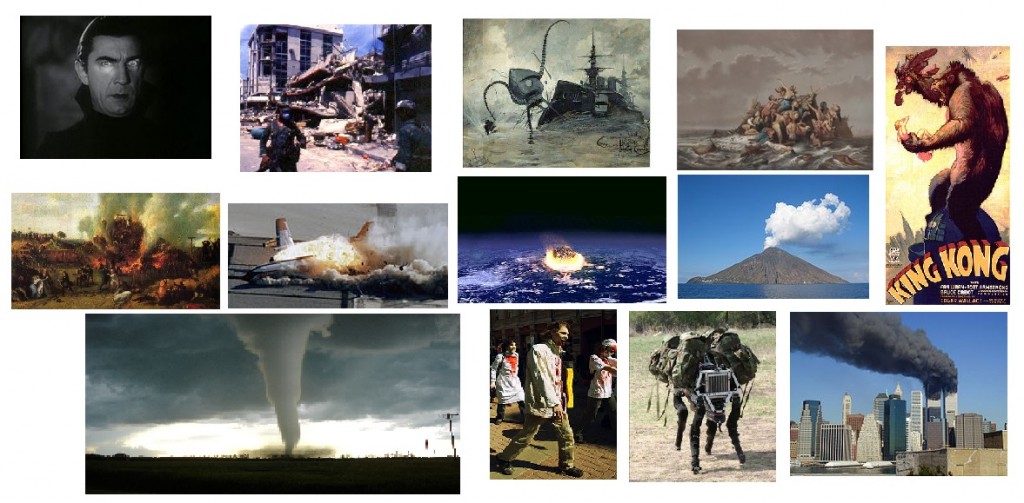
Disasters can be natural, as with floods or tsunamis, hurricanes, tornadoes, other significant storms, earthquakes, volcanoes, extreme climate change, asteroid or comet collisions, etc.
The disaster could be an accident, such as a shipwreck, airplane crash, train wreck, industrial accident, etc. A car crash probably wouldn’t count, since the disaster really should involve a large number of people.
There are other disasters that aren’t natural, and aren’t really accidents either. Let’s call them calamities, and separate them into plausible and less-plausible scenarios. The plausible ones include pandemics, terrorist attacks, major wars, economic collapse, and loss of electricity.
The less-plausible calamities (my own risk assessment; yours might differ) include: alien invasion, uncontrolled release of technology (such as nanotechnology, robot uprising, creation of a black hole, creation of a super-disease or super-creature, etc.), zombie apocalypse, “return” of vampires or werewolves, and attacks by menacing (usually gigantic) animals.
Themes
You’ll find some common themes in disaster stories. Here’s a partial list.
• Despite how far humans have progressed, we need reminding we are small and weak creatures in a big, dangerous universe.
• As disaster looms, people will react differently, going through the Kübler-Ross ‘Five Stages of Grief’ at different rates.
• A large-scale disaster will collapse the normal societal structure, and other structures will form.
• A disaster brings together strangers who must form a team with a common purpose, such as survival.
• A main character must overcome a personal fear or other psychological flaw and rise to the situation.
• A former leader cannot cope with the disaster; a new and unlikely leader must take charge.
• Often the protagonist’s main goal is either survival (of a group) or rescue of others.
• There are good and bad human reactions to disasters, and the characters who react badly often (though not always) meet a bad end. For example, preparation is better than assuming an unchanging future; clear thinking is better than panic, teamwork is better than uncaring self-centeredness; natural leadership is better than using a chaotic situation to claim power; focusing on the goal is more productive than blaming or finding fault.
Purpose
Why do people read disaster stories? These are among the reasons:
• It’s a chance to “experience” the disaster in a safe way, without having to endure it for real.
• The stories can be taken as metaphors for how we can deal with the smaller-scale mishaps of daily life.
• The tales can be metaphors for some perceived societal defect, as in H.G. Wells’ War of the Worlds.
• The stories offer lessons in preparation as old as the ant & grasshopper fable.
Conclusion
 I would classify only one of my stories as a true disaster tale. “The Finality” appeared in the anthology 2012 AD by Severed Press. In it, a scientist discovers that time itself is coming to an end, not just on Earth but throughout the universe, and there’s nothing anyone can do about it. But just maybe the Mayans were trying to tell us something about that.
I would classify only one of my stories as a true disaster tale. “The Finality” appeared in the anthology 2012 AD by Severed Press. In it, a scientist discovers that time itself is coming to an end, not just on Earth but throughout the universe, and there’s nothing anyone can do about it. But just maybe the Mayans were trying to tell us something about that.
May all your disasters be the written kind; that’s the hope of—
Poseidon’s Scribe
 “After the Martians” takes place in the world of Wells’ story, but sixteen years have passed since the alien attack. In my tale, humans make use of the Martian technology, especially the fighting machines, to fight World War I.
“After the Martians” takes place in the world of Wells’ story, but sixteen years have passed since the alien attack. In my tale, humans make use of the Martian technology, especially the fighting machines, to fight World War I.