Would you go on a writer’s retreat? I’ve blogged about them before, but that post took the form of a warning to set reasonable expectations for what you’ll accomplish.
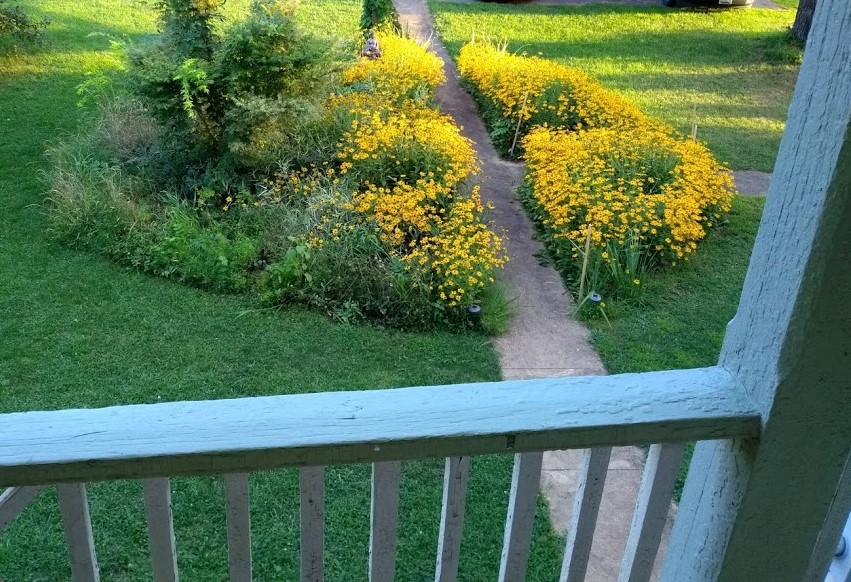
This weekend, while on a retreat, I’ll put on a more positive spin and discuss the benefits. I’ve retreated to an old house in a small rural town with three other writers—the members of my critique group. Here’s a view from the house’s balcony.

The house stands an hour and a half away from my home, where I usually write. The perspective, the atmosphere, the ambiance, is different here. I like to think it sends my mind down different grooves and lets my thoughts wander strange and unexplored byways.
There’s something invigorating about being among other writers, too. When not writing, we sit and talk. It’s fun to learn of their struggles and dreams, to celebrate their victories and commiserate over their defeats.
Non-writers have their own hobbies, of course, and join with like-minded hobbyists for weekends away. But their weekends are not like those of writers. If you could be here with us, you’d see us each in our own corner of the house, quietly busy with laptop or pen. At the moment, we’d rather talk to you, our readers, through our written words than to each other through spoken ones.
Does that sound odd? Pathetic? Rude? Introverted? Boring? Perhaps it would, to non-scribblers. To a writer, it is bliss. Here, for one glorious weekend, the urgencies of life do not interrupt, the excuses for not writing are absent, the schedule collapses to just one task.
There’s something too, about a change in perspective. It unshackles the mind. If you always write in the same chair, the same room, the same desk, is it any surprise that each of your stories seems like the others? Similar characters, similar plots, similar settings? For this reason, while writing at home, I sit in different chairs in different rooms. But this retreat, to a location I’ve never been, grants me a fresh outlook.
Retreats come in different flavors, of course. Some are more like writer workshops, with an expert providing occasional instruction. Some are solitary, where the writer goes unaccompanied to a remote locale. Each of these has pros and cons.
Your retreats need not be frequent, or expensive. My group goes only about every two to three years, and never to the same place twice. We’re mindful of costs and share the monetary burden. For us, the point is not to enjoy breathtaking scenery or to visit nearby attractions. All we need is quiet time. That’s worth emphasizing: Quiet. Time. Need ‘em both.
So, writer, consider a retreat. Withdraw from the daily demands of chores, work, and family. View things from a different angle for awhile. Socialize with other writers who strive, like you, to sharpen their scribbling skills. You might find you benefit as much from it as does—
Poseidon’s Scribe