Some time ago I wrote about finding your writing voice. Recently I read a post by Jessica Wildfire and it forced me to think deeper.
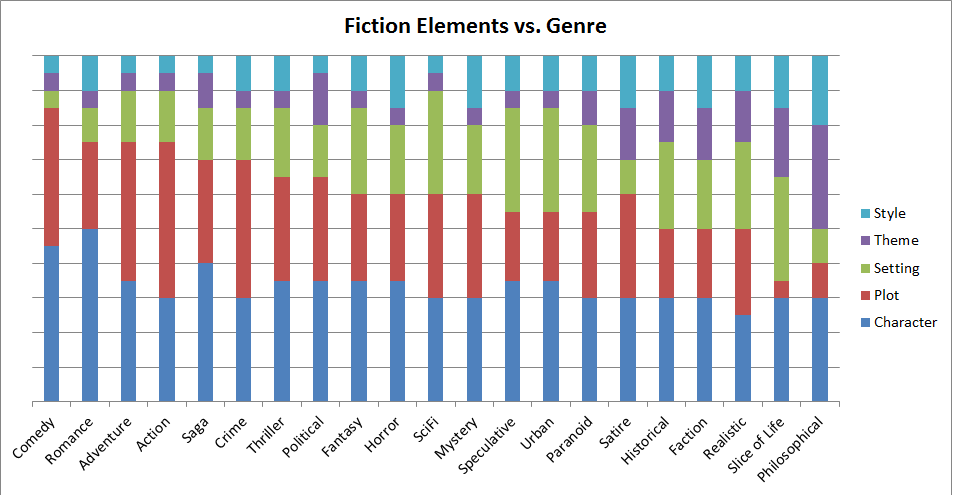
In my original post, I said a writer’s voice included two aspects: the stuff she writes about, and the way she writes it. In other words, (1) the topics and (2) the style. My suggestions on choosing topics are still sound. But Ms. Wildfire introduced some new thoughts about style.
Her 11-item list of style principles is so good I won’t repeat it here and will merely urge you to read her post. (Here’s that link again.) I’m just going to emphasize the part I found most disruptive.
She suggests reading Steven Pinker’s The Sense of Style, and I intend to do that. But she goes on to advise writers to toss The Elements of Style in the garbage.

Really, Jessica? Throw away my copies of Strunk and White? I couldn’t bear it.
I understand why she says that. The Elements of Style dates from a century ago, and contains numerous rules presented in a way that sounds rigid, overly prescriptive, and archaic. I’m guessing those are the parts she ‘hate-reads’ to her students as counter-examples.
But the overall message of Strunk and White, the vital essence of the work, is timeless and I hope Ms. Wildfire would agree. Elements is a plea for the writer to keep the reader always in his thoughts. Yes, your job as a fiction writer is to entertain, but to do that, you must first be understood.
As you look over Ms. Wildfire’s 11 principles of style, you’ll see she doesn’t care much for the old rules—the ones about grammar and showing rather than telling. But what comes through in her principles is a message Strunk and White would agree with. Write for the reader. Never confuse or bore the reader.
She advises writers to tell their stories in a voice readers can connect with. To do that, listen to the way real people talk. Notice the flow of words, the rhythms of their speech. If faced with a choice between clarity and correct grammar, opt for clarity. Delete the boring parts and cut to the chase.
Okay, Ms. Wildfire, I’ll follow most of your advice. But I’ll never throw away the Strunk & White I got back in 1976. I consult it occasionally and re-read it just a couple of months ago. Elements will remain on the bookshelves of—
Poseidon’s Scribe

 My list differs from hers, since it’s borne of my own experiences. Moreover, I’m sure there are plenty of unlisted items I’m still getting wrong, that hinder me from greater success.
My list differs from hers, since it’s borne of my own experiences. Moreover, I’m sure there are plenty of unlisted items I’m still getting wrong, that hinder me from greater success.