You should know the motivation of each fictional character you create. What do they desire? What inner need compels them to act the way they do? I’ve blogged about motivation before, and I’ll build on that today.
Motivation versus Goals
Every major character may pursue a goal, too, but that differs from motivation. A goal is the outcome a character seeks, and motivation is why the character wants it.
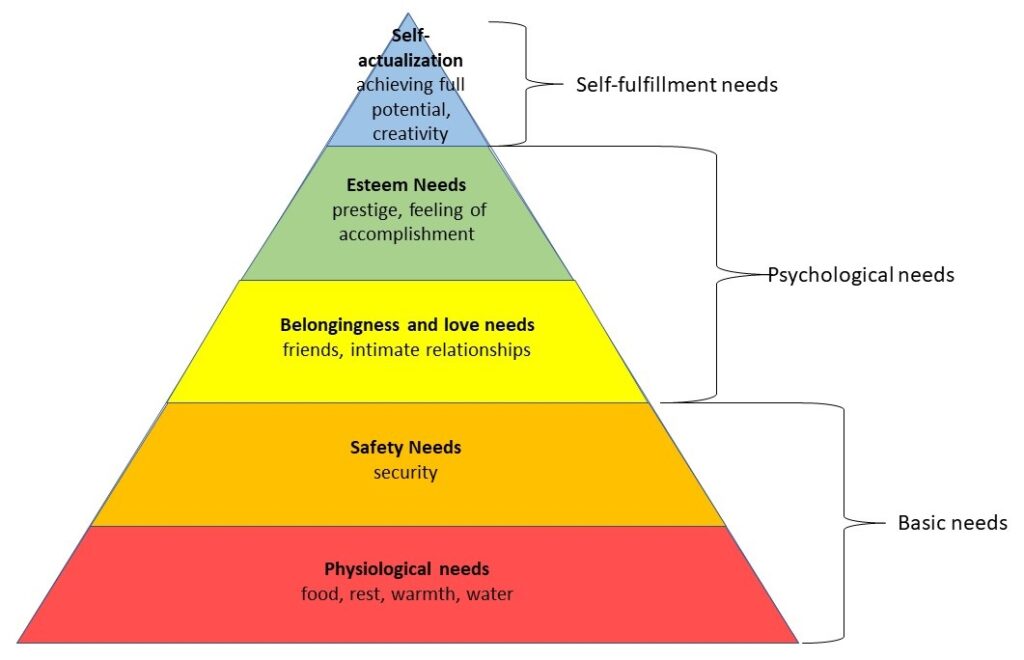
Maslow’s Hierarchy
In my earlier post, I mentioned Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. The pyramid shape suggests a character must meet lower-level needs before pursuing higher levels. If an antagonist or other circumstance deprives a character of a lower-level need, the character will revert down to that need and pursue it.
Russell’s Theory
The British philosopher Bertrand Russell discussed motivations (calling them desires) in his 1950 speech accepting the Nobel Prize in Literature. He focused on the motivations of political leaders, because these, he thought, influenced human history the most. If you include a political leader in your fiction, Russell’s thoughts may interest you.
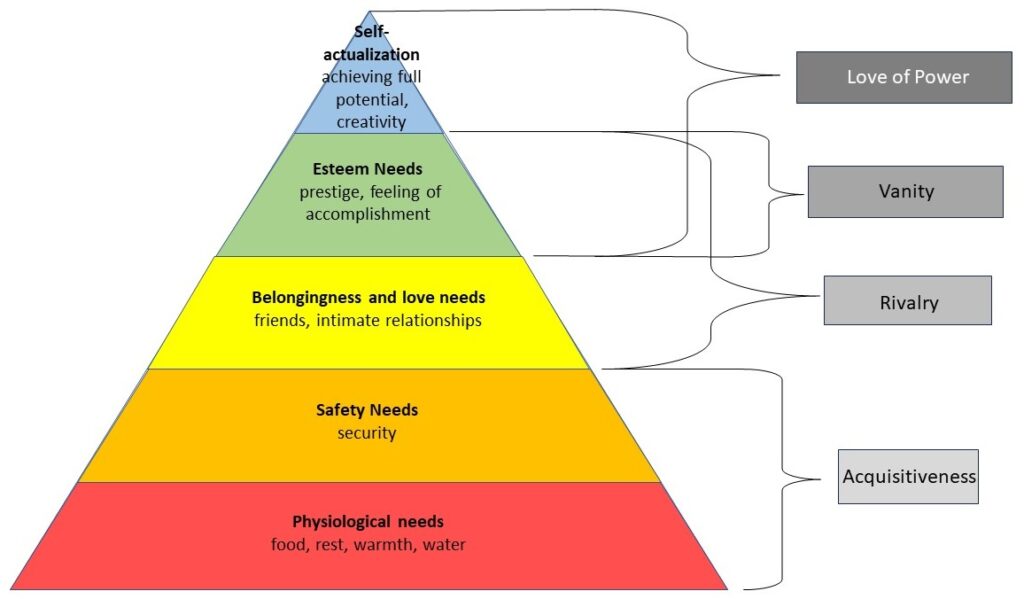
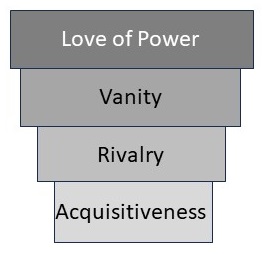
The philosopher named four major desires of political leaders—acquisitiveness, rivalry, vanity, and love of power. Put another way:
- acquisitiveness = I want your stuff
- rivalry = I want to surpass you
- vanity = I want you to worship me
- love of power = I want to control you
As Maslow did, Russell put his list of desires in a specific order, but in a more negative way. Perhaps an inverted pyramid makes more sense, for he ordered his group by strength. He rated acquisitiveness the weakest and love of power the strongest.
Moreover, he considered these needs insatiable. Like a snowball rolling downhill, the more you feed any of those needs, the bigger they get. No satisfied contentment awaits at the end.
Combining the Theories
Despite the differing approaches, I see parallels between Maslow’s positive list and Russell’s negative one. Acquisitiveness connects to Psychological and Safety needs—both concern material things and feeling secure. Rivalry connects to Belonging and Esteem—both concern relating with others. Vanity also connects to Esteem as well—both concern how the character is seen by others. Love of Power connects to both Esteem and Self-Actualization—both concern the achievement of full potential through creativity.
It’s Complicated
Perhaps, in trying to categorize and group motivations, both Maslow and Russell oversimplified matters. Humans exhibit a wide array of motivations, not just the ones listed by those two thinkers. Your fictional characters may act out of any motivation you choose, from an infinite list.
As you create characters, you may find Maslow’s pyramid and Russell’s list useful as a starting point. Feel free to add nuance and variation when determining what drives your characters.
Whatever my own motivation, concluding this blogpost is the immediate goal of—
Poseidon’s Scribe

I have a different set of four drives I’ve worked with. It dates back to an early 20th century sociologist named W.I. Thomas. The list overlaps somewhat with the one proposed by Lawrence and Nohria in the business-oriented book “Driven.” It also overlaps a bit with Maslow’s list. These are my names, not Thomas’s: power, prestige, status, significance; bonding, love, friendship, group identity; new experience, learning, discovery, novelty; security, safety, routine, preservation.
Thanks for the comment. That’s a great list. With such a wide spectrum of possible drives/motivations, it’s natural to try to group them into categories. As writers, though, that’s unnecessary. Just pick the motivation for your character that makes sense for the story. Or choose the motivation first and imagine the story you can write with that character in it.