When contrary facts collide with opinions, opinions should change, but often resist. I experienced that while reading this post by author Catherine Nichols about the good guy/bad guy myth.
My Former View
Prior to reading that post, I’d thought of ancient stories and folk tales as excessively moral. Peopled with characters wholly good or bad, the old yarns instructed readers in proper moral behavior. (And the moral of the story is…) Good guy wins because he’s good—bad guy loses because he’s bad.
I thought of these stories as immature, unsophisticated. We tell children simple stories of clearly-defined good and evil to help them make sense of a complex world, and to point them in a morally right direction.
In my understanding, Shakespeare changed that. He gave the world more complex characters, neither wholly good nor bad, deeper and more realistic. Sigmund Freud carried the movement further. After Freud, bad guys couldn’t practice evil for its own sake. They needed origin stories, psychological explanations for turning to the dark side, thus making them not wholly bad.
That led to our modern era, where stories tend toward the amoral, outside the moral/immoral spectrum. That’s what I thought, and even blogged about before.
A View Overturned
Ms. Nichols made the opposite case, and her post jarred my neuron signals from their accustomed paths. The ancient tales, she said, didn’t focus on morality or values much. Characters acted in accordance with their personality quirks, not in obedience to some moral code.
Citing examples such as the Iliad, Norse mythology, and familiar fairy tales, she asserted that old stories made no attempt to pit good against evil, or even teach moral lessons.
Modern stories, by contrast (particularly those depicted on screen), emphasize the white hat/black hat distinction and assign moral virtues to the characters, giving them codes of conduct to live by.
Nichols said modern re-telling of old stories insert morality where it hadn’t existed in the original. She cited the examples of Robin Hood, King Arthur, and Thor, where later writers assigned moral codes to characters who hadn’t possessed them in the original versions.
Toward a New Understanding
Which version is true? Did ancient authors write stories laden with morality, intended to instruct, while we modern sophisticates have transcended that? Or did past writers spin yarns without regard for moral teachings while today, we feel the need to issue good or evil badges to our characters? Is one type of story more evolved, more worldly, than the other? Or perhaps both views oversimplify the issue, cherry-picking examples to fit a theory?
Let’s start by assuming storytellers existed in every era of humanity, all the way back to the origins of language. With the advent of writing, storytellers documented their tales.
We may also assume people through the ages have differed in practices, cultures, customs, and values. Perhaps these differences influenced each community’s preferences for story types. Only those tales that resonated with a group got passed down. As storytellers and writers experimented, they discovered what worked for their audiences.
If a writer caught a cultural turning point, a readiness for something fresh and different, that writer met the new need. Other writers rode that wave, too.
I’m suggesting that moral and amoral stories have existed in all times and places. They either catch on or not depending on the prevailing preferences of their current, local marketplace.
Whether stories endure beyond the time and culture of their writing does not depend on the degree of morality in them. Rather, classics live on because they say something important about the universal aspects of human nature.
So What?
Meanwhile, at your own keyboard, you’re wondering how this esoteric discussion affects you. Where’s the actionable advice?
Okay, here it is. You may find it interesting to ponder the history of storytelling and debate the ebb and flow of moral and amoral stories. Or you may not. Just write the story within you, and I’ll write the story within—
Poseidon’s Scribe

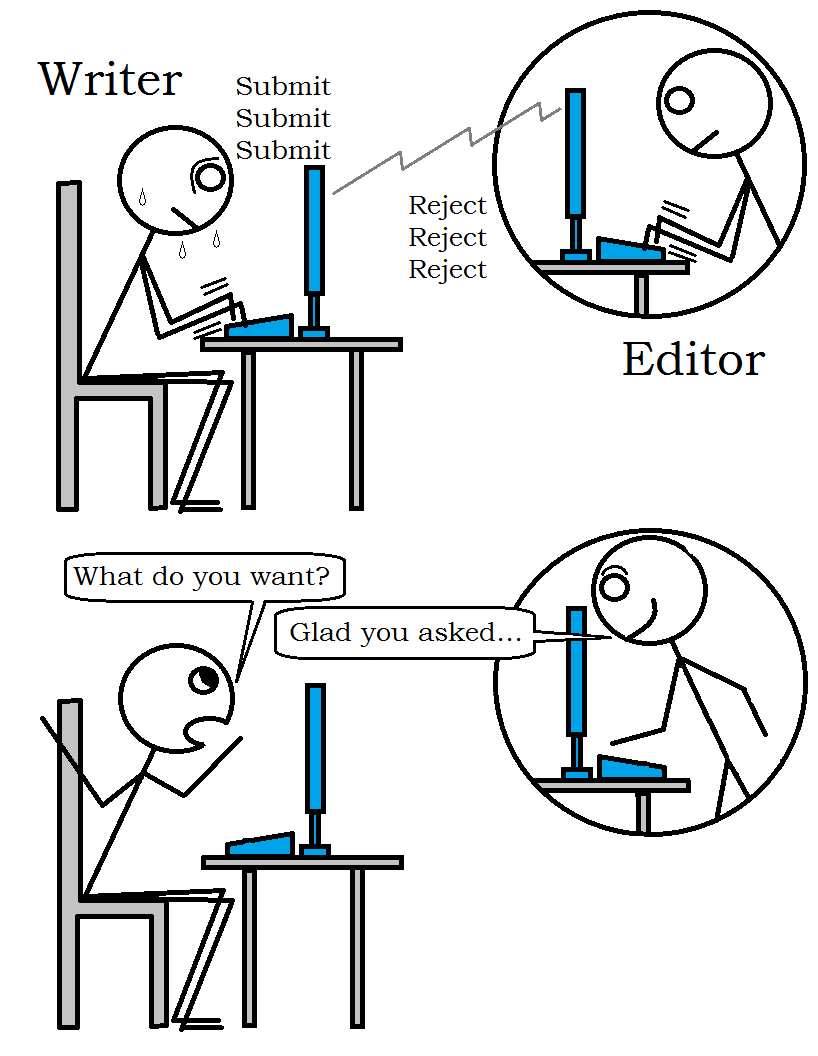
 Today I’ll consider the topic of characters getting too big for their britches, and assuming a bigger (or different) role than the one planned for them. When this happens in your writing, should you take it as a good thing or a bad thing?
Today I’ll consider the topic of characters getting too big for their britches, and assuming a bigger (or different) role than the one planned for them. When this happens in your writing, should you take it as a good thing or a bad thing?






 experience is based solely on twenty years of being in small, amateur, face-to-face critique groups; not writing workshops, classes, or online critique groups; so the following advice is tuned to that sort of critique.
experience is based solely on twenty years of being in small, amateur, face-to-face critique groups; not writing workshops, classes, or online critique groups; so the following advice is tuned to that sort of critique.